Navigating Through Freight Seasonality: The Crucial Role of Strategic Planning
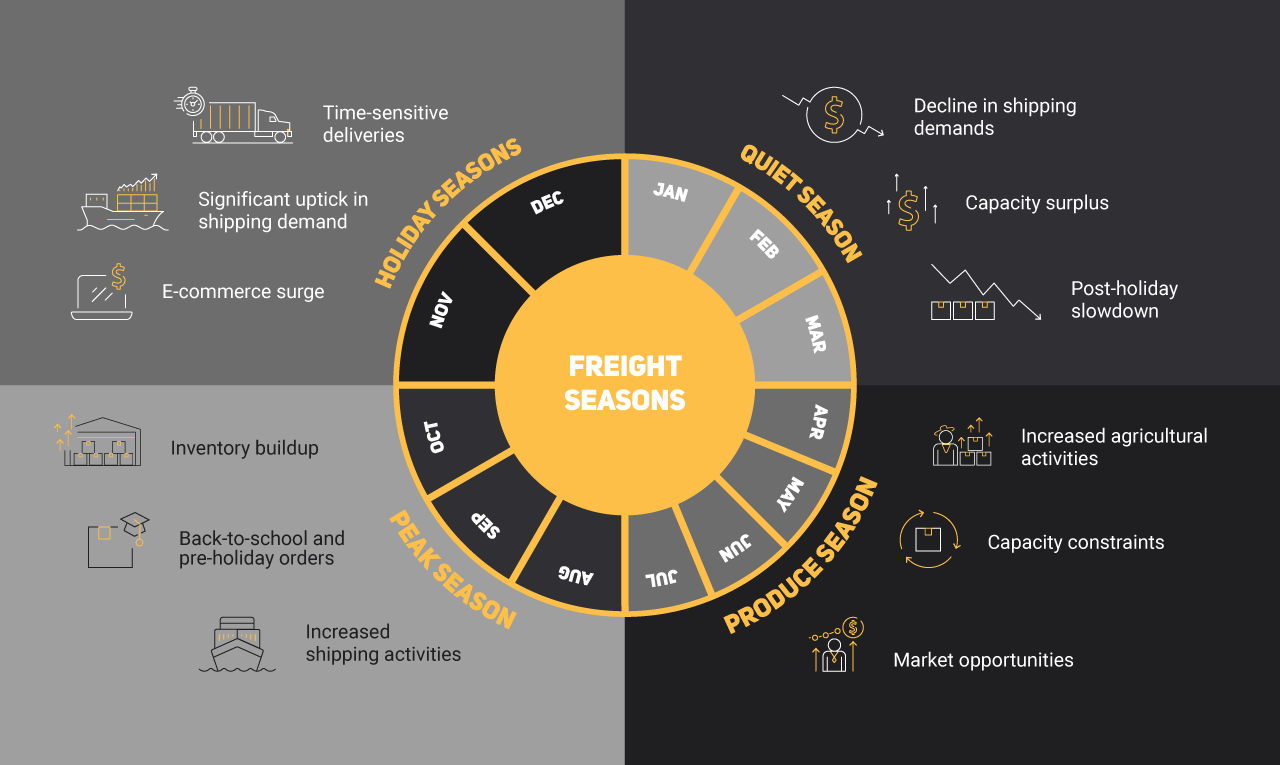
Freight seasonality refers to the predictable patterns of highs and lows in shipping activity that occur throughout the year. These patterns are influenced by a myriad of factors, including holidays, weather conditions, and industry-specific events. For businesses involved in transportation and logistics, failing to account for these seasonal variations can lead to disruptions in the supply chain, increased costs, and missed opportunities.
The nature of freight seasonality greatly affects supply chain operations. It becomes critical for organizations to comprehend and navigate the ebbs and flows of freight seasonality as they work to satisfy consumer needs and maximize efficiency. The following article explores the nuances of freight seasonality and emphasizes how crucial strategic planning is to adjusting to the demand swings in freight over the course of the year.
Detailed Overview of Freight Seasons
Freight seasons refer to periods of time when the demand for shipping and transportation services experiences fluctuations based on various factors. These seasons are influenced by economic, environmental, and cultural factors, among others.
Logistics and supply chain management depend on an understanding of and ability to anticipate freight seasons. It enables companies to efficiently allocate resources, plan ahead, and maximize productivity whether there is a high or low demand for transportation services.

Quiet Season
The period from January to March is often considered a quiet freight season in various industries. Several factors contribute to this trend, affecting transportation and logistics operations.
Factors contributing to quiet аreight season:
- Seasonal demand fluctuations. Following the peak holiday season, there is typically a decrease in consumer demand for goods. This results in reduced production and shipment activities across various industries. Also, adverse winter weather conditions, such as snowstorms and icy roads, can disrupt transportation networks and slow down freight movements. This can lead to delays and a general decrease in shipping activities.
- Inventory management. Many businesses conduct year-end inventory assessments and implement strategies to reduce excess stock. This can result in lower demand for freight services during the early months of the year. Some industries experience a temporary slowdown in production during the first quarter as they adjust their operations based on the previous year’s performance and market trends.
- Economic factors. Companies often start the new fiscal year with budget constraints, leading to careful expenditure management. This may result in a reduced need for shipping services during the initial months. Periods of economic uncertainty or downturns can impact consumer spending and industrial production, leading to decreased demand for freight services.
- Regulatory changes. Many businesses conduct annual reviews to ensure compliance with industry regulations. This process may lead to temporary disruptions in shipping schedules and reduced freight volumes. Increased focus on compliance with environmental regulations or changes in shipping regulations can affect the overall cost of freight operations, potentially leading to decreased shipping activity.
- Market-specific trends. Certain industries may have specific seasonal cycles or trends that influence freight demand during the first quarter. Understanding these industry-specific factors is crucial for logistics planning.
Mitigation strategies for stakeholders:
- Enhanced planning. Stakeholders can optimize logistics operations by planning for reduced demand during the quiet freight season, adjusting staffing levels, and optimizing transportation routes. Businesses can strategically plan their inventory levels to align with expected demand, minimizing excess stock during the quieter months.
- Weather preparedness. Transportation providers can develop robust contingency plans to address potential disruptions caused by adverse weather conditions, ensuring the continuity of freight services.
- Flexible resource management. Employers can implement flexible staffing arrangements to match the reduced demand, ensuring efficient resource allocation during the quiet freight season.

Produce Season
The period from April to July marks the peak of the produce season, a crucial time for the agricultural and transportation industries. This season is characterized by increased demand for fresh fruits and vegetables, creating a surge in agricultural activities, transportation requirements, and market dynamics.
- Agricultural activities. Farmers begin planting crops in the early spring, and by April, the first harvests start, continuing through July. The season witnesses a diverse range of fruits and vegetables, including berries, melons, tomatoes, corn, and more. Different regions experience varying climates and growing conditions, leading to a staggered harvest schedule for various produce items. This diversity contributes to the availability of a wide range of fresh produce during the season.
- Increased demand. As warmer weather arrives, there is a natural shift in consumer preferences towards lighter, fresher, and more seasonal produce. This change in demand impacts grocery stores, restaurants, and other food-related businesses. The produce season aligns with increased awareness of health and wellness, driving higher demand for fresh fruits and vegetables among consumers.
- Transportation and logistics. The surge in agricultural production necessitates efficient transportation of produce from farms to distribution centers and retailers. Trucking, rail, and shipping industries experience heightened activity during this period. Due to the perishable nature of many fruits and vegetables, maintaining the cold chain becomes crucial. Refrigerated transportation ensures that produce reaches its destination in optimal condition.
- Market dynamics. The abundance of fresh produce during the season can lead to price fluctuations, influenced by factors such as weather conditions, crop yields, and transportation costs. Increased supply often leads to heightened competition among growers and distributors. Effective marketing strategies become essential to stand out in a crowded market.
- Labor intensity. The produce season creates a surge in demand for seasonal agricultural labor, including planting, harvesting, and packing activities. Farming communities often rely on temporary workers to meet this increased demand. The produce season provides employment opportunities in rural areas, attracting seasonal workers who contribute to the success of the harvest.
- Regulatory compliance. Given the focus on food safety, there is increased scrutiny on the handling and transportation of fresh produce. Compliance with regulations ensures the integrity of the supply chain and consumer safety.

Peak Season
The period from August to October marks the peak season for various industries, characterized by heightened consumer demand, increased manufacturing activities, and a surge in logistics and transportation operations. Here are the aspects of this season:
- Back-to-school and retail demand. August signals the back-to-school season, driving increased demand for school supplies, clothing, and electronics. Retailers experience a surge in sales as parents and students prepare for the academic year. Many retailers strategically offer promotions, discounts, and seasonal sales to attract customers, contributing to a spike in overall consumer spending.
- E-commerce and holiday preparation. With the rise of e-commerce, online retailers experience a surge in orders as consumers turn to the internet for convenience and a wider range of products. Some consumers start early holiday shopping during the peak season, leading to increased production and distribution activities for various goods.
- Manufacturing and Production. Manufacturers often ramp up production during the peak season to meet the rising demand for consumer goods, including electronics, clothing, and household items. Companies optimize their supply chains to ensure a smooth flow of raw materials and finished products, collaborating closely with suppliers and logistics partners.
- Logistics and Transportation. The surge in consumer demand necessitates an increase in shipping volumes across various modes of transportation, including trucking, rail, air, and sea freight. Logistics providers focus on efficient inventory management to prevent stockouts and delays, ensuring timely deliveries to meet customer expectations.
- Seasonal employment. Industries experiencing a peak season often hire temporary workers to handle increased demand in manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution. The influx of seasonal workers presents challenges in terms of training, supervision, and maintaining high operational standards during the busy period.
- Inventory planning and management. Retailers and manufacturers engage in strategic stockpiling to ensure an adequate supply of popular products during peak demand periods. Efficient inventory turnover becomes crucial to manage stock levels effectively and avoid overstocking or stockouts.
- Marketing and promotions. Companies invest in marketing and advertising campaigns to promote seasonal sales, discounts, and special offers, attracting a larger customer base. Establishing brand visibility and differentiation in the market becomes essential during the competitive peak season.
- Supply Chain Resilience. Businesses focus on supply chain resilience by implementing contingency plans to address unexpected disruptions, such as weather events, transportation delays, or geopolitical challenges.

Holiday Season
The period from November to December marks the holiday season, a time of increased consumer spending, festive celebrations, and heightened economic activity. Here are the key aspects of this season:
- Consumer spending and retail sales. The holiday season is synonymous with gift-giving traditions, leading to a significant uptick in consumer spending on a wide range of products, including electronics, clothing, toys, and home goods. These shopping events, occurring in late November, kick off the holiday shopping season with massive discounts and promotions, both in physical stores and online.
- E-commerce surge. The convenience of online shopping continues to drive a surge in e-commerce during the holiday season. Retailers offer exclusive online deals, and consumers increasingly turn to digital platforms for gift purchases. E-commerce companies focus on efficient shipping and fulfillment operations to meet the demand for timely deliveries, often collaborating with logistics partners.
- Seasonal employment. The holiday season prompts an increase in temporary employment in retail, warehousing, and logistics sectors to manage the influx of shoppers and higher shipping volumes. Companies also bolster customer service teams to handle inquiries, returns and provide support during the busy season.
- Festive decorations and seasonal products. Retailers stock up on festive decorations, holiday-themed merchandise, and specialty items catering to the spirit of celebration. Businesses engage in festive marketing campaigns to create a sense of holiday excitement, utilizing themed advertisements and promotions.
- Travel and hospitality industry. The holiday season sees a surge in travel as families reunite and individuals take vacations. Airports, hotels, and other travel-related services experience heightened demand. Accommodation providers and travel agencies gear up for increased bookings, offering special holiday packages and promotions.
- Food and beverage. Families and individuals stock up on food and beverages for festive meals and celebrations, leading to increased demand for groceries. The hospitality industry experiences a surge in restaurant reservations, catering services, and takeout orders for holiday gatherings.
- Supply chain challenges. Retailers and manufacturers must carefully manage inventory levels to meet the increased demand while avoiding stockouts or excess stock. Efficient coordination of logistics and transportation is crucial to ensure that products reach stores and customers on time, especially during peak shipping periods.
- Community and charity initiatives. The holiday season often fosters a spirit of generosity, with businesses and individuals engaging in charitable activities, donations, and community outreach programs. Companies may align their holiday initiatives with corporate social responsibility, contributing to the well-being of communities.
Strategic Planning for Seasonal Shifts
Logistics experts must anticipate and adjust to changing seasons in order to guarantee dependable and effective supply chain operations. Logistics teams may increase the accuracy of demand forecasting by working with stakeholders, analyzing previous data, and utilizing cutting-edge technologies by implementing efficient demand forecasting tactics. Logistics experts can more easily adapt to changes in demand by employing just-in-time methods, optimizing inventory levels, and encouraging flexibility in operations. These strategies all contribute to efficient capacity planning. Establishing robust connections with carriers is of equal importance; upholding transparent communication, reaching adaptable agreements, and employing key performance indicators (KPIs) foster cooperative alliances that harmonize the concerns of logistics suppliers and carriers. Moreover, improving real-time visibility and overall supply chain efficiency requires embracing technology, automating processes, and utilizing data analytics for insights.
Logistics experts should concentrate on risk management and backup plans in order to strengthen resilience. It is possible to identify prospective obstacles, such as weather occurrences and geopolitical variables, by conducting comprehensive risk assessments. Proactively responding to possible disruptions is ensured by creating thorough backup plans that include warehousing arrangements, backup transportation options, and alternative suppliers. Logistics experts dedicated to constant observation, cooperation with stakeholders, and flexibility are better equipped to handle the challenges posed by seasonal fluctuations in demand, resulting in a strong and flexible supply chain.
In Conclusion
To guarantee the seamless and effective flow of goods throughout the year, businesses and customers alike must have a thorough awareness of freight seasonality. Logistics professionals may improve the overall reliability of supply chain operations by anticipating issues, optimizing resources, implementing strategies, and recognizing the patterns and trends associated with different seasons. This knowledge becomes especially important at peak times when demand fluctuations can have a major influence on logistics networks, such as the holiday season or times of increased agricultural production.
For customers seeking logistics services that prioritize experience and expertise in navigating freight seasonality, Carolina Logistics stands as a reliable and seasoned partner. With our extensive experience, we understand the intricacies of seasonal variations and offer tailored solutions to meet the unique demands of each period. Our commitment to proactive planning, innovative technologies, and strong relationships with carriers ensures that our customers receive top-notch logistics services, even during the most challenging seasonal fluctuations. Choose Carolina Logistics for a partner that not only comprehends the dynamics of freight seasonality but also consistently delivers reliable and efficient logistics solutions to meet your business needs.