The Most Popular Trucks and Trailers in the Trucking Industry

As the foundation of the global supply chain, trucks are essential to the logistics and transportation industry. Their ability to effectively transport commodities over a range of distances, linking producers, distributors, and retailers, accounts for their significance. To fulfill the unique needs and problems presented by various cargo kinds and transportation requirements, this industry needs a diversity of trucks.
The logistics and transportation sector’s diversity of vehicles guarantees that it can effectively handle a wide range of freights and meet specific transportation needs. Trucks are essential to the worldwide movement of goods because they can be customized for any freight type or used as last-mile delivery vehicles.
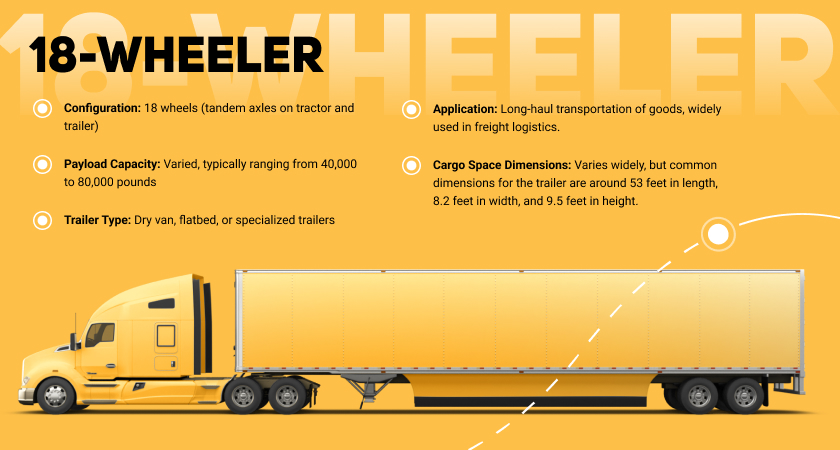
Semi-Trailer Truck (18-Wheeler)
A semi-trailer truck, commonly known as an 18-wheeler or big rig, is a large vehicle used for transporting goods. It consists of a tractor unit (powered by an engine) and a semi-trailer (a trailer without a front axle). The combination of the tractor and semi-trailer gives the 18-wheeler its distinct appearance. These trucks are commonly used for long-haul transportation due to their large cargo capacity and efficiency.
Key features:
- Tractor unit (Cab). The front part of the truck contains the engine, driver’s cabin, and controls. The cab may have one or more sleeping compartments for long-haul drivers.
- Semi-trailer. The rear part of the truck that carries the cargo. Semi-trailers can vary in length, with common types being 48 feet or 53 feet long. They are typically detachable, allowing for flexibility in loading and unloading.
- Axle configuration. 18-wheelers have a total of 18 wheels, distributed across the tractor and semi-trailer. The tractor usually has two steer wheels in the front and two or more axles with dual wheels in the rear. The semi-trailer has multiple axles with dual wheels to distribute the weight of the cargo.
- Payload capacity. 18-wheelers are designed to carry large and heavy loads, making them suitable for long-distance transportation.
- Engine and powertrain. Equipped with powerful diesel engines to provide sufficient torque for hauling heavy loads. Transmission systems are designed to optimize fuel efficiency and handle various terrains.
- Fuel efficiency. Modern semi-trucks are designed with fuel efficiency in mind, using advanced technologies to reduce fuel consumption during long journeys.
Common uses in trucking:
- Freight transportation. 18-wheelers are widely used for transporting goods over long distances between cities and across states. They play a crucial role in the logistics and supply chain industry.
- Cross-country shipping. Ideal for transporting goods across vast distances, connecting manufacturing centers, distribution hubs, and retail locations.
- Time-sensitive deliveries. Long-haul trucking is often preferred for time-sensitive shipments, where quick and reliable transportation is essential.
- Intermodal transportation. Semi-trailer trucks are often used in conjunction with other modes of transportation, such as trains and ships, for intermodal shipping.
Most popular semi-truck manufacturers in the US:
- Freightliner (Daimler AG). One of the largest manufacturers of heavy-duty trucks in North America. Offers a wide range of trucks for various applications, including long-haul and vocational use.
- Kenworth (PACCAR). Known for producing premium-quality trucks with a focus on customization for customer needs. Offers a range of models suitable for different hauling requirements.
- Peterbilt (PACCAR). Specializes in custom-built trucks with a reputation for durability and performance. Offers both on-highway and vocational trucks.
- Volvo Trucks (Volvo Group). Produces a variety of trucks, including those designed for long-haul transportation. Known for safety features and fuel efficiency in their vehicles.
- Mack Trucks (Volvo Group). Well-known for producing heavy-duty trucks, including those used in long-haul applications. Mack trucks are recognized for their ruggedness and reliability.
- International Trucks (Navistar International). Offers a range of trucks for various purposes, including long-haul and regional transportation. Known for their versatility and innovative features.
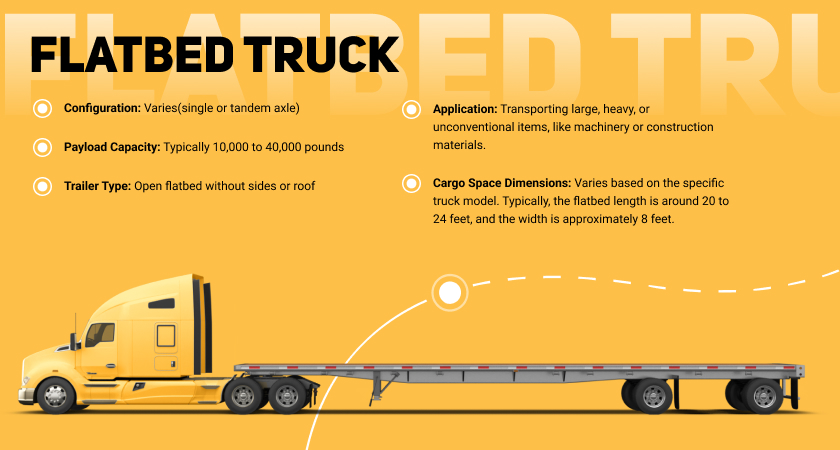
Flatbed Truck
A flatbed truck is a type of truck that features an entirely flat, level bed or platform with no sides or roof. This open design allows for easy loading and unloading of cargo from the sides and rear of the vehicle. Flatbed trucks are commonly used to transport oversized or irregularly shaped loads that may not fit into enclosed trailers. They provide versatility for a wide range of industries due to their open design, making them suitable for carrying large, heavy, or unconventional items.
Key features:
- Open flatbed. The defining feature is the flat and open cargo bed without sides or a roof. Allows for easy loading and unloading of goods from any side of the truck.
- Strapping and tie-down points. Equipped with anchor points, tie-downs, and winches to secure cargo safely. Essential for securing loads of various shapes and sizes during transportation.
- Versatility. Well-suited for transporting oversized or irregularly shaped items, machinery, construction materials, and other loads that may not fit into enclosed trailers.
- Accessibility. Provides easy access for forklifts and cranes to load and unload cargo.
- Heavy-duty construction. Designed to handle heavy loads and withstand the demands of transporting large, cumbersome items.
- Removable sides and stakes. Some flatbed trucks may have removable sides or stakes that can be added to convert the flatbed into a stake bed, providing additional cargo containment options.
Common uses in trucking:
- Construction materials. Flatbed trucks are commonly used to transport construction materials such as steel beams, pipes, lumber, and concrete forms.
- Machinery and equipment. Ideal for hauling heavy machinery, oversized equipment, and vehicles that may not fit into traditional enclosed trailers.
- Large or unconventional cargo. Well-suited for transporting items with irregular shapes, sizes, or dimensions that cannot be accommodated by enclosed trailers.
- Building materials. Commonly employed to transport materials like steel, aluminum, concrete panels, and other construction supplies.
- Pipelines and oil industry. Used for transporting pipes, drilling equipment, and other materials related to the oil and gas industry.
Most popular trailer configurations:
- Standard flatbed trailer. A basic flatbed trailer with a flat, open cargo bed and no sides or roof.
- Drop deck trailer. Features a lower deck towards the rear of the trailer, providing additional clearance for taller cargo.
- Extendable flatbed trailer. Allows for the extension of the trailer bed to accommodate longer loads.
- Stretch trailer. Similar to an extendable flatbed, a stretch trailer can be adjusted to accommodate longer loads but typically features more sections for flexibility.
- Conestoga trailer. A flatbed trailer with a rolling tarp system that provides some level of protection for the cargo while maintaining the open design.
- Double drop trailer. Features a lower deck both at the front and rear, allowing for the transportation of exceptionally tall items.
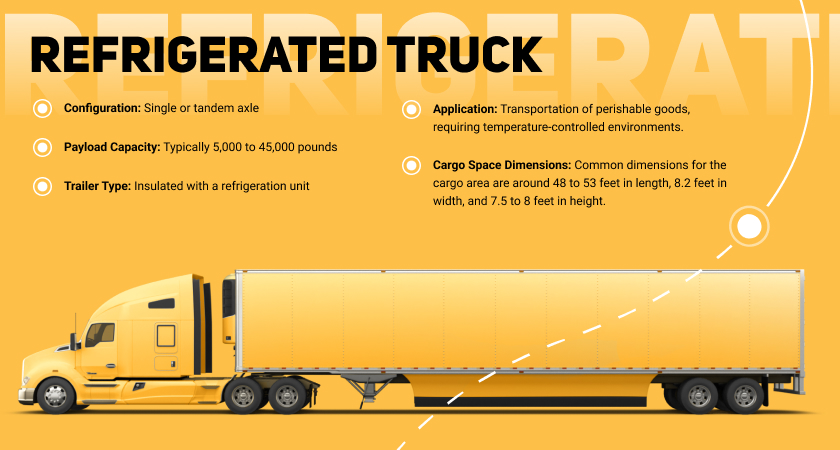
Refrigerated Truck (Reefer)
A refrigerated truck, commonly referred to as a “reefer,” is a specialized type of truck designed to transport goods that require a controlled temperature environment. These trucks are equipped with a refrigeration unit to maintain specific temperature conditions, typically cold or frozen, throughout the transportation of perishable items. Reefers are crucial for industries such as food and pharmaceuticals, where maintaining a consistent and controlled temperature is essential to preserve the quality and safety of the transported goods.
Key features:
- Insulated Walls. Reefer trucks have insulated walls to minimize heat transfer and maintain the desired temperature inside the cargo area.
- Refrigeration Unit. The primary feature is the refrigeration unit mounted on the truck or integrated into the trailer. The unit can be powered by the truck’s engine or have a separate power source.
- Temperature Control Systems. Equipped with advanced temperature control systems to regulate the internal temperature within a specific range. Some reefers have multi-zone capabilities to accommodate different temperature requirements for various types of cargo.
- Airflow Systems. Designed with airflow systems to ensure uniform distribution of cool air throughout the cargo area.
- Temperature Monitoring. Often equipped with sophisticated monitoring systems to track and record the temperature levels during transit.
- Rear and Side Doors. Typically features rear and side doors for easy loading and unloading of goods while maintaining temperature control.
- Durable Flooring. The cargo area usually has a durable and easy-to-clean floor to meet hygiene standards.
Common uses in trucking:
- Food transportation. Reefer trucks are widely used to transport perishable food items, including fresh produce, dairy products, meat, and frozen goods.
- Pharmaceuticals. Crucial for transporting pharmaceutical products that require specific temperature conditions to maintain their efficacy and safety.
- Chemicals and biotechnology. Used for transporting temperature-sensitive chemicals, biotechnology products, and other goods with strict temperature requirements.
- Medical supplies. Reefer trucks play a role in transporting medical supplies, including vaccines and other temperature-sensitive healthcare products.
- Floral industry. Essential for transporting flowers and plants, as they require temperature control to prevent wilting and maintain freshness.
Most popular trailer models in the US:
- Van reefer. A common type of refrigerated trailer featuring a box-like structure with insulated walls and a refrigeration unit mounted on the front.
- Drive-in reefer. A trailer with doors at both ends, allowing for drive-through loading and unloading while maintaining temperature control.
- Straight truck reefer. Smaller trucks with a refrigerated cargo area suitable for local deliveries and smaller quantities of perishable goods.
- Container reefer. Reefer containers are used in intermodal transportation, providing a refrigerated environment for goods transported via ships, trains, and trucks.
- Dual-temperature reefer. Trailers with dual-temperature zones are used for the transportation of goods with different temperature requirements in the same load.
- Multi-temperature reefer. Offers multiple temperature zones within the same trailer, providing flexibility for transporting a variety of perishable goods with different temperature needs.
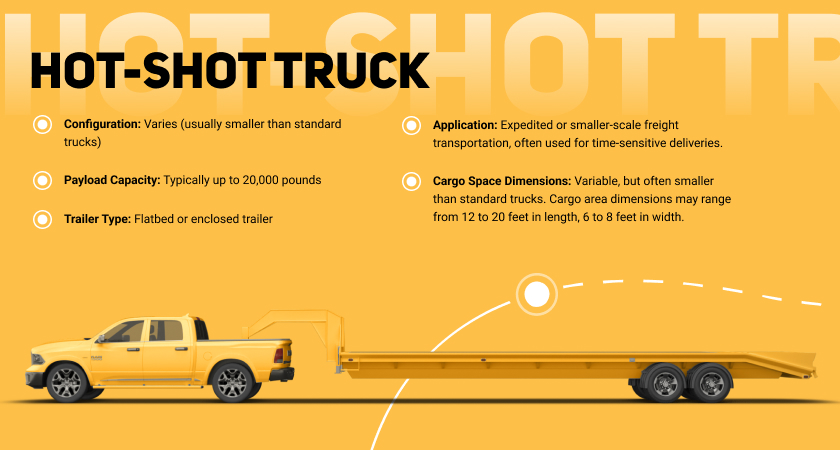
Hot-Shot Truck
Hot-shot trucks refer to smaller, often non-commercial trucks used for the transportation of smaller and time-sensitive loads. These trucks are typically smaller than traditional long-haul trucks but are still equipped for hauling freight over long distances. The term “hot shot” originated from the idea of quickly transporting urgent or expedited shipments, often in response to time-sensitive demands.
Key features:
- Compact size. Hot shot trucks are generally smaller than standard long-haul trucks, making them more maneuverable and suitable for transporting smaller loads.
- Gooseneck or bumper pull trailers. Hot shot trucks commonly use gooseneck or bumper pull trailers, allowing for quick and easy attachment and detachment.
- Diverse load capacities. These trucks can handle a variety of loads, ranging from small, urgent shipments to larger and heavier cargo.
- Versatility. Hot shot trucks are versatile and can be used for various applications, including hauling construction materials, equipment, and other time-sensitive deliveries.
- Expedited freight services. Often employed for expedited freight services, where quick and timely delivery is essential.
- Independent operators. Many hot shot truck drivers operate independently or as part of small fleets, providing flexibility for shippers with unique and urgent transportation needs.
- Adaptability. Hot shot trucks can adapt to different routes and delivery schedules, making them suitable for a range of logistics and transport requirements.
Common uses in trucking:
- Oil and gas industry. Hot shot trucks are frequently used in the oil and gas industry to transport equipment, tools, and parts to remote locations quickly.
- Construction. Ideal for transporting construction materials, tools, and equipment to construction sites where traditional large trucks may face access challenges.
- Agriculture. Used for transporting agricultural supplies, equipment, and perishable goods in a timely manner.
- Expediting services. Hot shot trucks are commonly employed for expediting services, fulfilling urgent delivery requirements for various industries.
- Emergency parts delivery. Used in cases where emergency parts need to be delivered quickly to minimize downtime in manufacturing or other industries.
Popular hot shot models in the US:
The choice of hot shot trucks can vary, as many operators use a variety of truck models and trailer configurations based on their specific needs. Some popular models include:
- Ford F-Series. Trucks like the Ford F-350 or F-450 are commonly used for hot shot hauling due to their reliability, power, and towing capabilities.
- Chevrolet Silverado/GMC Sierra HD. Heavy-duty models like the Chevrolet Silverado and GMC Sierra HD are popular choices for hauling smaller loads over long distances.
- Ram Trucks. Ram offers heavy-duty models like the Ram 2500 and Ram 3500, known for their towing capacity and durability.
- Dodge/Ram 4500 and 5500 Chassis Cab. These chassis cab models are often upfitted with specialized bodies for hot shot hauling.
- Nissan Titan XD. The Nissan Titan XD is a heavy-duty pickup truck that combines power and versatility, making it suitable for hot shot applications.
- Chevrolet/GMC Medium-Duty Trucks. Medium-duty trucks like the Chevrolet Silverado 4500HD and 5500HD, as well as their GMC counterparts, offer additional payload capacity for hot shot hauling.
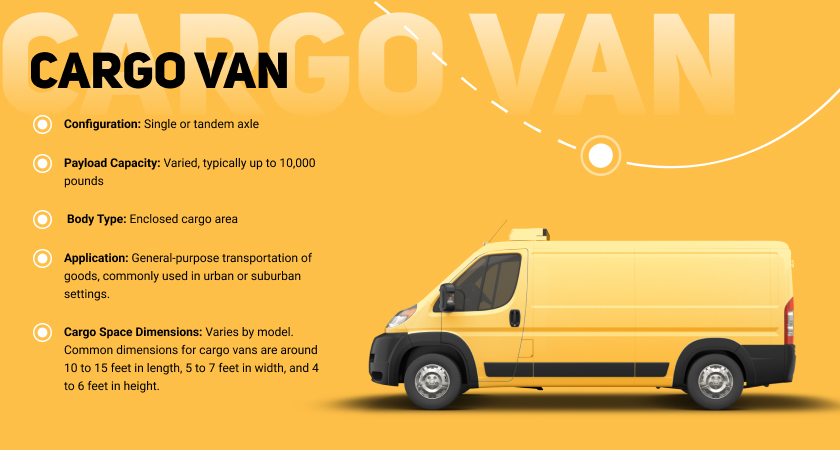
Van
Cargo vans are light commercial vehicles designed primarily for transporting goods and cargo. They are characterized by their enclosed cargo area, typically located behind the driver’s cabin. Cargo vans come in various sizes and configurations, and they are widely used for local deliveries, courier services, and small-scale logistics. These vehicles are essential for businesses that require efficient and compact transportation solutions for their goods.
Key features:
- Enclosed cargo space. Cargo vans have a dedicated and enclosed cargo area separate from the driver’s cabin, providing security and protection for transported goods.
- Compact size. Designed to be more compact than larger delivery trucks, cargo vans are maneuverable and suitable for navigating urban and suburban environments.
- Variety of sizes. Cargo vans are available in various sizes, from compact vans suitable for smaller loads to larger models with increased payload capacity.
- Rear and side access. Typically equipped with rear and/or side doors for easy loading and unloading of cargo.
- Flat load floor. The cargo area often features a flat load floor, making it easy to stack and organize goods.
- Fuel efficiency. Cargo vans are generally more fuel-efficient compared to larger trucks, making them cost-effective for short-distance deliveries.
- Customization options. Many cargo vans offer options for interior customization, including shelving, partitions, and other organizational features to suit specific business needs.
Common uses in trucking:
- Local deliveries. Cargo vans are commonly used for local deliveries of goods, including packages, food, and other small items.
- Courier and express services. Ideal for courier and express delivery services, transporting documents, parcels, and time-sensitive goods.
- Service and maintenance. Used by service and maintenance professionals to transport tools, equipment, and parts to job sites.
- Retail and e-commerce. Many retail and e-commerce businesses utilize cargo vans for last-mile deliveries to customers.
- Contracting and trades. Contractors and tradespeople often use cargo vans to transport tools, materials, and equipment to job sites.
- Mobile businesses. Some cargo vans are converted into mobile businesses, such as mobile workshops, food trucks, and service vehicles.
Most popular cargo van models in the US:
- Ford Transit. The Ford Transit is a versatile and popular cargo van available in various configurations, sizes, and payload capacities.
- Mercedes-Benz Sprinter. Known for its quality and customizable options, the Mercedes-Benz Sprinter is a favorite for businesses with diverse cargo transportation needs.
- Chevrolet Express/GMC Savana. The Chevrolet Express and GMC Savana are traditional cargo van models with reliable performance and ample cargo space.
- Ram ProMaster. The Ram ProMaster offers a front-wheel-drive design, maximizing cargo space and ease of loading.
- Nissan NV. The Nissan NV is a durable and spacious cargo van available in various sizes to accommodate different business requirements.
- Mercedes-Benz Metris. A smaller alternative from Mercedes-Benz, the Metris, offers a good balance of cargo space and maneuverability.

Small Refrigerated Truck or Van
Small refrigerated trucks or vans are vehicles designed for the transportation of perishable goods while maintaining a controlled and refrigerated environment. These vehicles are typically smaller in size compared to larger refrigerated trucks and are well-suited for businesses that require the transport of smaller quantities of temperature-sensitive items. They play a crucial role in the cold chain logistics, ensuring that products like food, pharmaceuticals, and other perishables are delivered in optimal condition.
Key features:
- Refrigeration unit. Small refrigerated trucks or vans are equipped with a built-in refrigeration unit to maintain specific temperature conditions inside the cargo area.
- Insulated cargo area. The cargo area is insulated to minimize heat transfer and ensure temperature consistency.
- Compact size. These vehicles are smaller in size, making them more maneuverable and suitable for navigating urban and suburban areas.
- Temperature control systems. Equipped with temperature control systems to regulate and monitor the internal temperature, ensuring that perishable goods remain within the desired temperature range.
- Rear and side access. Typically have rear and/or side access points for easy loading and unloading of cargo.
- Versatility. Small refrigerated trucks or vans are versatile and suitable for a variety of industries, including food delivery, pharmaceutical distribution, and catering.
- Fuel efficiency. Due to their smaller size, these vehicles often exhibit better fuel efficiency compared to larger refrigerated trucks.
Common uses in trucking:
- Food and beverage delivery. Small refrigerated trucks or vans are commonly used for delivering perishable food and beverages to restaurants, grocery stores, and other retail outlets.
- Pharmaceutical distribution. Ideal for transporting temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals and medical supplies to pharmacies, hospitals, and clinics.
- Catering services. Used by catering businesses to transport prepared meals and perishable ingredients to event locations.
- Floral industry. Small refrigerated vans are utilized to transport flowers and plants, maintaining freshness during transportation.
- Dairy products delivery. Well-suited for delivering dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt to retailers and consumers.
- Online grocery delivery. With the rise of online grocery shopping, small refrigerated trucks or vans play a role in delivering fresh and frozen groceries directly to consumers.
Most popular small refrigerated truck or van models in the US:
- Ford Transit Connect Refrigerated Van. The Ford Transit Connect is a compact van that can be upfitted with a refrigeration system, making it suitable for smaller deliveries.
- Mercedes-Benz Metris Refrigerated Van. The Mercedes-Benz Metris, when equipped with a refrigeration unit, offers a good balance of size and functionality for small refrigerated transport.
- Chevrolet Express/GMC Savana Refrigerated Van. The Chevrolet Express and GMC Savana are available in various configurations, including refrigerated versions for smaller cargo.
- Nissan NV200 Refrigerated Van. The Nissan NV200 is a compact van that can be converted into a refrigerated vehicle, commonly used for urban deliveries.
- Ram ProMaster City Refrigerated Van. The Ram ProMaster City is a small van that can be adapted for refrigerated transport, offering versatility in urban settings.
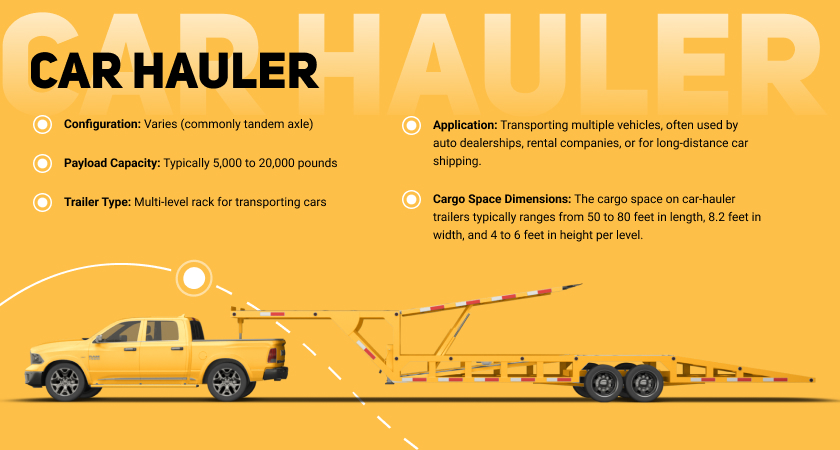
Car Hauler
Car hauler trucks, also known as car carriers or auto transporters, are specialized vehicles designed for transporting multiple vehicles simultaneously. These trucks are equipped with trailers or platforms that allow them to efficiently transport cars, trucks, or other vehicles from one location to another. Car haulers are commonly used in the automotive industry, including for new vehicle deliveries to dealerships, transporting used cars, and facilitating vehicle relocations for individuals.
Key features:
- Multiple vehicle capacity. Car hauler trucks are designed to carry multiple vehicles at once, either on open trailers or enclosed platforms.
- Ramps and loading systems. Equipped with ramps or loading systems to facilitate the efficient loading and unloading of vehicles onto and off the truck.
- Securing mechanisms. Feature various securing mechanisms such as wheel straps, tire stops, and ratchet straps to ensure the vehicles remain stable during transportation.
- Variety of configurations. Car haulers come in various configurations, including open trailers, enclosed trailers, and multi-level racks, catering to different types of vehicles and customer preferences.
- Hydraulic systems. Some car haulers are equipped with hydraulic systems that allow for easy tilting or lowering of the trailers to facilitate loading and unloading.
- Durable construction. Built with durability in mind, car hauler trucks are designed to withstand the weight and dimensions of multiple vehicles.
- Vehicle protection. Enclosed car haulers provide protection against weather, debris, and road elements, ensuring the vehicles arrive in the same condition as when loaded.
Common uses in trucking:
- New car deliveries. Car haulers are frequently used to transport new vehicles from manufacturing plants to dealerships, ensuring a steady supply of fresh inventory.
- Used car transport. Used car dealerships and auctions often employ car haulers to transport pre-owned vehicles between locations.
- Vehicle relocation services. Car haulers facilitate the relocation of individuals’ vehicles when moving across long distances or when they purchase a vehicle from a different location.
- Exotic and classic car transport. Enclosed car haulers are commonly used to transport high-value or classic cars, providing protection against the elements during transit.
- Rental car logistics. Car haulers assist in the logistics of relocating rental vehicles between rental branches to meet customer demand.
- Auto shows and exhibitions. Car haulers play a role in transporting vehicles to auto shows, exhibitions, and events where multiple cars need to be moved efficiently.
Most popular car hauler configurations in the US:
- Open car trailers. These trailers have an open design and are commonly used for transporting standard vehicles, such as sedans, SUVs, and light trucks.
- Enclosed car trailers. Enclosed trailers provide protection against weather and road elements, making them suitable for transporting high-value or classic cars.
- Multi-level rack trailers. These trailers have multiple levels, allowing for the transportation of more vehicles in a single load, often used for smaller cars or motorcycles.
- Single-level platform trucks. Some car haulers have a flat platform without stacking, suitable for transporting larger or heavier vehicles, including trucks and SUVs.
- Hydraulic tilt trailers. Trailers equipped with hydraulic systems that allow for easy tilting, simplifying the loading and unloading process.
- Auto transporters with sleeper cabs. Some car hauler trucks come with sleeper cabs, allowing the drivers to rest during long-distance hauls.
In Conclusion
Comprehending the different kinds of trucks is essential to appreciating the varied functions they fulfill in the international supply chain. Every type of truck is built with certain features to meet the demands of various industries and load specifications. These vehicles operate together to build an intricate network that is necessary for the movement of goods, whether it is due to the effectiveness of long-haul semi-trailer trucks, the adaptability of cargo vans, the accuracy of hot shot trucks, or the particular capabilities of car haulers and refrigerated trucks.
This understanding is important since it helps to optimize supply chain and logistics processes. Employing the appropriate truck type for a given activity can help firms increase productivity, cut expenses, and guarantee the safe and prompt delivery of goods. Every kind of truck makes a distinct contribution to the complex web of international trade, from the transportation of automobiles to the delivery of perishable products to the distribution of goods to final customers.
More generally, trucks are the foundation of the global supply chain, linking producers, suppliers, retailers, and end users. Their function is especially important in guaranteeing the supply of commodities, promoting economic expansion, and satisfying the demands of a market that is continuously changing. Businesses are better equipped to make decisions, adjust to shifting logistical requirements, and support the smooth operation of the interconnected global supply chain when they have a sophisticated grasp of the many types of trucks.